ns5gt-> get vr trust-vr protocol ospf config
VR: trust-vr RouterId: 10.0.0.1
----------------------------------
set protocol ospf
set enable
set area 0.0.0.10
set area 0.0.0.10 range 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 advertise
exit
set interface trust protocol ospf area 0.0.0.10
set interface trust protocol ospf enable
set interface trust protocol ospf cost 1
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf area 0.0.0.0
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf enable
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf cost 1
ssg5-serial-wlan-> get vr trust-vr protocol ospf config
VR: trust-vr RouterId: 10.0.0.2
----------------------------------
set protocol ospf
set enable
set area 0.0.0.20
set area 0.0.0.20 range 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 advertise
set area 0.0.0.20 range 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 advertise
exit
set interface bgroup0 protocol ospf area 0.0.0.20
set interface bgroup0 protocol ospf enable
set interface bgroup0 protocol ospf cost 1
set interface bgroup1 protocol ospf area 0.0.0.20
set interface bgroup1 protocol ospf enable
set interface bgroup1 protocol ospf cost 1
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf area 0.0.0.0
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf enable
set interface tunnel.1 protocol ospf cost 1
Dave's IT Blog
Sunday, March 17, 2013
ScreenOS Route-Based VPN Configuration
Configuration process:
1. Create a tunnel interface (Prefer on untrust zone).
2. Create an IKE gateway (Phase 1)
3. Create an AutoKey IKE (Phase 2)
4. Configure routing (Tunnel interface as the gateway)
5. Create a policy (If tunnel interface and source address are not on the same zone)
Troubleshooting:
FW-> ping <destination interface IP> from <source interface>
FW-> get route ip <destination interface IP>
FW-> get ike cookie
FW-> get sa active
1. Create a tunnel interface (Prefer on untrust zone).
2. Create an IKE gateway (Phase 1)
3. Create an AutoKey IKE (Phase 2)
4. Configure routing (Tunnel interface as the gateway)
5. Create a policy (If tunnel interface and source address are not on the same zone)
Troubleshooting:
FW-> ping <destination interface IP> from <source interface>
FW-> get route ip <destination interface IP>
FW-> get ike cookie
FW-> get sa active
Thursday, December 13, 2012
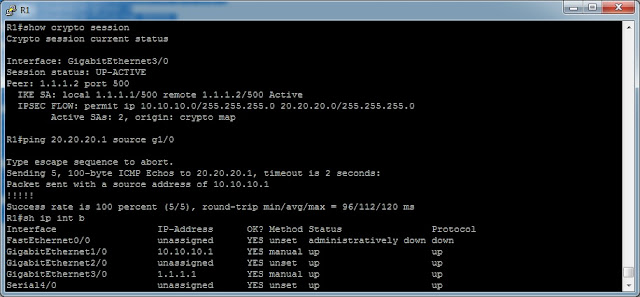
[Cisco] IPSec Site to Site VPN on IOS router (Sample 1)
(1) Configure ISAKMP (ISAKMP Phase 1)
(2) Configure IPSec (ISAKMP Phase 2, ACLs, Crypto MAP)
(2) Configure IPSec (ISAKMP Phase 2, ACLs, Crypto MAP)
Configure ISAKMP (IKE) - (ISAKMP Phase 1)
R1(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R1(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R1(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R1(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R1(config-isakmp)# group 2
R1(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
R1(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.2
Creating crypto ACL
R1(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
Create IPSec Transform (ISAKMP Phase 2 policy)
R1(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
R1(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
Create Crypto Map
R1(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R1(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.2
R1(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R1(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
R1(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R1(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.2
R1(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R1(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
Apply Crypto Map to the Public Interface
R1(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R1(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
R1(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R1(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Add default route
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
R2 Config:
R2(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R2(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R2(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R2(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R2(config-isakmp)# group 2
R2(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
!
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.1
!
R2(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
!
R2(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
!
R2(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R2(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.1
R2(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R2(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
!
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R2(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
R2(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R2(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R2(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R2(config-isakmp)# group 2
R2(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
!
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.1
!
R2(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
!
R2(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
!
R2(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R2(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.1
R2(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R2(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
!
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R2(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Friday, November 2, 2012
RHEL5.8 and SSR2011 Testbed
Node A
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.12/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.12/24
Private: eth2: 192.168.205.12/24
Node B
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.13/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.13/24
Private: eth2: 192.168.205.13/24
SAN:
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.20/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.20/24
Check current LVM config
Boot up the server with CustomSRD.
Use fdisk to create the same partitions as the original server.
lvm pvcreate /dev/{sda2,sdb1,sdc1}
lvm pvdisplay
lvm vgcreate -s 32M VolGroup00 /dev/{sda2,sdb1,sdc1}
lvm vgdisplay
lvm lvcreate -L 27.84G -n LogVol00 VolGroup00
lvm lvcreate -L 1.97G -n LogVol01 VolGroup00
lvm lvdisplay
mkfs.ext3 /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
mkfs.ext3 /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol01
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.12/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.12/24
Private: eth2: 192.168.205.12/24
Node B
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.13/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.13/24
Private: eth2: 192.168.205.13/24
SAN:
Public: eth0: 192.168.159.20/24
iSCSI: eth1: 192.168.70.20/24
Restore the system:
Capture fdisk -l on original server.Check current LVM config
Boot up the server with CustomSRD.
Use fdisk to create the same partitions as the original server.
lvm pvcreate /dev/{sda2,sdb1,sdc1}
lvm pvdisplay
lvm vgcreate -s 32M VolGroup00 /dev/{sda2,sdb1,sdc1}
lvm vgdisplay
lvm lvcreate -L 27.84G -n LogVol00 VolGroup00
lvm lvcreate -L 1.97G -n LogVol01 VolGroup00
lvm lvdisplay
mkfs.ext3 /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
mkfs.ext3 /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol01
Some useful Linux commands
Check runlevel
$ who -r
Change runlevel
# vi /etc/inittab
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Format a SWAP partition:
# mkswap /dev/sda1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
iSCSI:
Discovering iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p <Group IP address>:3260
Logging in iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m node -l
#iscsiadm -m node -l -T <Complete Target Name> -p <Group IP>:3260
Example:
#iscsiadm -m node -l -T iqn.2001-05.com.equallogic:83bcb3401-16e0002fd0a46f3d-rhel5-test -p 172.23.10.240:3260
Logging out iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m node -u
#iscsiadm -m node -u -T <Complete Target Name> -p <Group IP address>:3260
Example:
#iscsiadm -m node -u -T iqn.2001-05.com.equallogic:83bcb3401-16e0002fd0a46f3d-rhel5-test -p 172.23.10.240:3260
Restart iSCSI service:
# /etc/init.d/iscsi restart
Delete old target:
iscsiadm -m node -p 192.198.1.148 --op=delete
Check connected target:
/var/lib/iscsi/nodes/
Server IQN:
# cat /etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
測試iSCSI target在Linux上的I/O速度。
# hdparm -tT /dev/sdb1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Network:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network
GATEWAY=your-ip
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0:0
IPADDR=192.168.1.7
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
NETWORK=192.168.1.0
ONBOOT=yes
NAME=eth0:0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
YUM Local Repo:
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-debuginfo.repo
[cdrom]
name=RHEL $releasever-$basearch CDROM
baseurl=file:///media/cdrom/Server
enabled=1
gpgchechk=1
gpgkey=file:///media/cdrom/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
$ who -r
Change runlevel
# vi /etc/inittab
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Format a SWAP partition:
# mkswap /dev/sda1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
iSCSI:
Discovering iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p <Group IP address>:3260
Logging in iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m node -l
#iscsiadm -m node -l -T <Complete Target Name> -p <Group IP>:3260
Example:
#iscsiadm -m node -l -T iqn.2001-05.com.equallogic:83bcb3401-16e0002fd0a46f3d-rhel5-test -p 172.23.10.240:3260
Logging out iSCSI Targets:
#iscsiadm -m node -u
#iscsiadm -m node -u -T <Complete Target Name> -p <Group IP address>:3260
Example:
#iscsiadm -m node -u -T iqn.2001-05.com.equallogic:83bcb3401-16e0002fd0a46f3d-rhel5-test -p 172.23.10.240:3260
Restart iSCSI service:
# /etc/init.d/iscsi restart
Delete old target:
iscsiadm -m node -p 192.198.1.148 --op=delete
Check connected target:
/var/lib/iscsi/nodes/
Server IQN:
# cat /etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
測試iSCSI target在Linux上的I/O速度。
# hdparm -tT /dev/sdb1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Network:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network
GATEWAY=your-ip
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0:0
IPADDR=192.168.1.7
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
NETWORK=192.168.1.0
ONBOOT=yes
NAME=eth0:0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
YUM Local Repo:
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-debuginfo.repo
[cdrom]
name=RHEL $releasever-$basearch CDROM
baseurl=file:///media/cdrom/Server
enabled=1
gpgchechk=1
gpgkey=file:///media/cdrom/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thursday, November 1, 2012
Hot add a NIC to a VM with a Linux guest OS
To configure the network card from the command line interface:
- The acpiphp module must be loaded for Linux to detect hot-added devices.
To load the acpiphp module, run this command:
modprobe acpiphp
- Run the kudzu command to ensure that the new hardware is detected and configured.
- Run this command to ensure that the network card is enabled:
ifup eth2 Note: eth2 is the new network card that has been added.
- To configure the network card, edit the ifcfg-eth2 file using a text editor.
To edit the file using vi editor, run this command:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth2
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)